I. Introduction
Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring is one of the most influential nursing theories shaping modern nursing practice. Developed by Jean Watson, it emphasizes the science of caring as a central aspect of the nursing profession. It highlights the importance of human care and caring in nursing, extending beyond physical treatment. The caring theory integrates the mind, body, and spirit in a caring relationship. The key concepts include:
- Transpersonal caring – a deep nurse–patient connection that transcends physical needs.
- Caritas and caritas processes – guiding principles for compassionate care process in professional nursing.
- Meets human needs holistically through human caring theory.
The Watson Caring Science Institute advances education, research, and application of the theory of human caring worldwide. The theory supports patient-centered approaches in the nursing profession. It bridges nursing practice and compassion with evidence-based care and encourages nurses to see caring as a healing science, not just a task. Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring strengthens the foundation of caring in nursing, reinforcing that the care process is as much about emotional and spiritual support as it is about physical healing.
II. Brief Biography of Jean Watson
A. Early Life and Education
- Jean Watson was born in West Virginia, where her early experiences shaped her passion for human care and compassion in health.
- She pursued nursing education at the University of Colorado, laying the foundation for her future contributions to nursing practice and nursing theories.
- Her academic training emphasized not only clinical skills but also the science of caring, which became central to her later work on Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring.
B. Career Milestones
- Watson became a professor and dean at the University of Colorado School of Nursing, where she influenced generations of the nursing profession.
- She founded the Watson Caring Science Institute, an organization dedicated to advancing the theory of human caring globally.
- Throughout her career, she published multiple books that expanded the understanding of caring in nursing, the care process, and caring theory.
- She developed the idea of transpersonal caring, which emphasizes a deep caring relationship between nurse and patient that goes beyond the physical to address emotional and spiritual human needs.
- Recognition of her work positioned her as one of the most influential figures in professional nursing.
C. Contributions to Nursing Theories
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring is considered a landmark in modern nursing theories, focusing on holistic care that integrates body, mind, and spirit.
- The theory introduces caritas and the caritas processes, guiding principles that define how nurses can provide meaningful, compassionate, and ethical care.
- Human caring theory emphasizes that true healing occurs within authentic nurse–patient connections, aligning with the idea that caring in nursing is more than technical treatment—it is a moral and spiritual commitment.
- Watson’s work reshaped nursing practice by establishing that the caring theory is essential to meeting both the physical and psychological human needs of patients.
- By framing care as the science of caring, Watson positioned nurses not only as caregivers but also as healers engaged in a higher calling of service.
- Today, Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring continues to inspire the nursing profession, guiding education, research, and clinical practice across the globe.
- The life and career of Jean Watson reflect a deep commitment to human caring theory. Her milestones, including the founding of the Watson Caring Science Institute, underscore how Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring transformed the values of professional nursing, making caring in nursing a central and enduring philosophy.
III. Overview of Watson’s Theory of Human Caring
A. Definition of the Theory
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring is a central model in modern nursing theories, emphasizing holistic human care.
- Developed by Jean Watson, the theory views nursing practice as more than medical intervention—it integrates compassion, spirituality, and healing.
- The theory of human caring highlights that true care supports physical, emotional, and spiritual human needs.
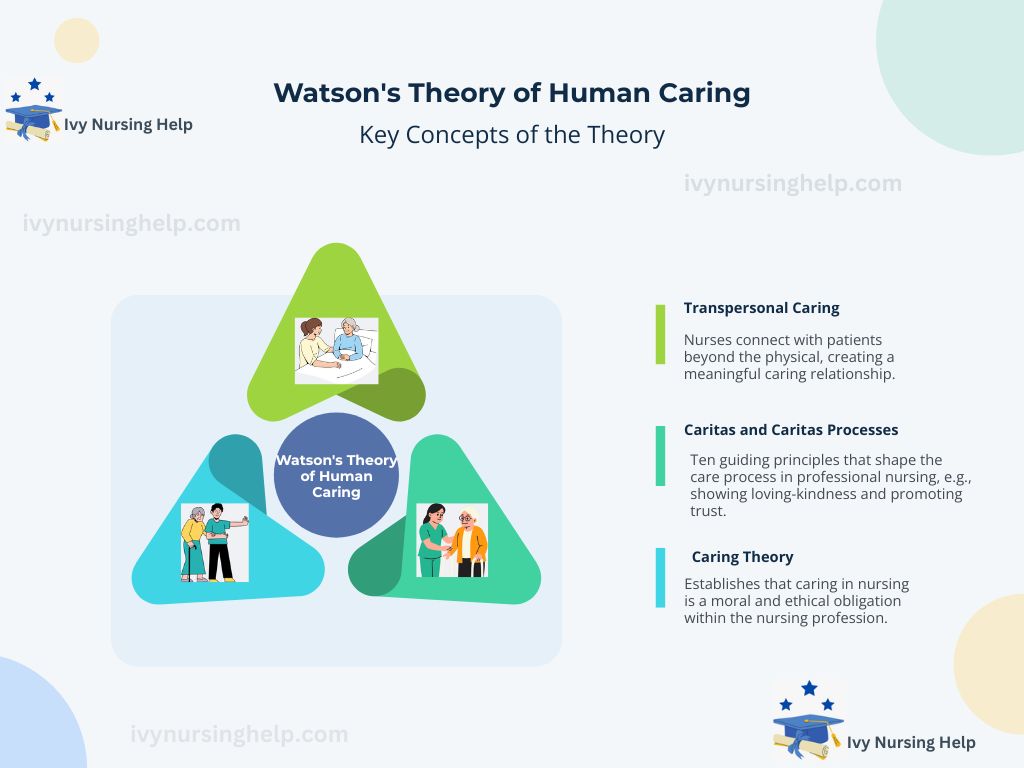
B. Key Concepts of the Theory
- Transpersonal caring – Nurses connect with patients beyond the physical, creating a meaningful caring relationship.
- Caritas and caritas processes – Ten guiding principles that shape the care process in professional nursing, such as showing loving-kindness, promoting trust, and meeting human needs holistically.
- Caring theory – Establishes that caring in nursing is a moral and ethical obligation within the nursing profession.
- Human caring theory – Recognizes that authentic healing requires mind-body-spirit unity, aligning with caring in nursing.
C. Watson’s Philosophy and Science of Caring
- Watson’s philosophy is grounded in the science of caring, positioning care as both an art and a discipline.
- The Watson Caring Science Institute advances education, research, and global practice of Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring.
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring emphasizes that nurses provide healing environments through respect, empathy, and compassion.
- By promoting professional nursing as a calling of service, the theory shifts focus from illness treatment to whole-person care.
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring continues to shape nursing practice, reinforcing the belief that authentic connections improve patient outcomes.
At its core, Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring underscores the value of caring in nursing, showing that the caring theory is not just an idea but a foundation for the nursing profession.
IV. Application of the Theory in Nursing Practice
A. Importance of Human Care in Nursing
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring stresses that human care is the foundation of the nursing profession.
- Care goes beyond physical treatment to address emotional, spiritual, and psychological human needs.
- This caring theory strengthens nursing practice by ensuring that patients experience dignity, compassion, and healing.
- Watson emphasizes that the science of caring is as critical as the science of curing.
B. Implementation in Nursing Care Settings
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring is applied across hospitals, clinics, and community health centers.
- Nurses use caritas processes—such as practicing kindness, fostering hope, and creating healing environments—in daily care process activities.
- Healthcare institutions guided by the Watson Caring Science Institute implement training to align professional nursing with the human caring theory.
- The focus is on holistic care, where caring in nursing addresses not only illness but the entire well-being of patients.
C. Role of Caring Relationships in Patient Outcomes
- A caring relationship built on trust and respect improves patient satisfaction and healing.
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring highlights transpersonal caring, where the nurse–patient connection transcends the physical and becomes spiritual and emotional.
- Evidence shows that patients cared for under this caring theory experience reduced stress, faster recovery, and stronger emotional resilience.
- By incorporating nursing theories like Watson’s, nurses fulfill their role as healers in professional nursing.
D. Examples of Caring Practices in Nursing
- Using caritas such as active listening, genuine presence, and empathy during every care process.
- Applying caritas processes to comfort patients facing chronic illness, anxiety, or end-of-life care.
- Nurses practicing Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring often integrate meditation, prayer, or quiet presence to support patients’ human needs.
- In nursing practice, these caring actions demonstrate the human caring theory in action and create lasting impacts on patient health.
The application of Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring transforms nursing practice into a holistic discipline that values the science of caring. By focusing on caring relationships, transpersonal caring, and caritas processes, the theory continues to shape the nursing profession and ensure that caring in nursing remains central to patient outcomes.
Achieve Excellence in Your Nursing Theory Paper
Struggling with your nursing theory research paper? Ivy Nursing Help delivers expertly written, well-structured, and original papers tailored to your needs. Elevate your grades—order now and experience professional academic support that makes a difference!
V. Application of the Theory in Nursing Education
A. Integration of Watson’s Theory into Nursing Curriculum
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring has become a vital part of many nursing programs worldwide.
- Nursing schools integrate the theory of human caring to teach students the importance of addressing physical, emotional, and spiritual human needs.
- The Watson Caring Science Institute provides resources and frameworks to incorporate caritas processes into classroom and clinical learning.
- By embedding caring theory into the curriculum, nursing students learn that caring in nursing is central to effective nursing practice.
B. Preparing Nursing Students for Professional Nursing Practice
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring helps prepare students for the demands of professional nursing by emphasizing the science of caring alongside technical skills.
- Students are taught transpersonal caring, which encourages deep connections and authentic caring relationships with patients.
- Exposure to human caring theory allows nursing students to value compassion, empathy, and holistic approaches within the nursing profession.
- Through structured care process exercises, future nurses develop not only competence but also a humanistic mindset.
C. Case Studies Demonstrating Caring Moments in Education
- Faculty often use case studies to demonstrate how Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring applies in real-life nursing practice.
- Examples include nursing students applying caritas and caritas processes in simulations or clinical rotations to meet diverse human needs.
- Case studies highlight instances of caring in nursing, such as listening to patients’ stories, showing presence, or offering comfort.
- These examples demonstrate that integrating caring theory into education yields better patient outcomes and more compassionate professionals.
By embedding Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring into the educational process, nursing programs nurture future nurses who embrace the science of caring. This ensures that nursing theories remain relevant, guiding both learning and the growth of the nursing profession.
VI. Strengths of Watson’s Theory of Human Caring
A. Promotion of Human Dignity and Quality of Nursing Care
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring highlights that patients are more than medical cases—they are human beings with emotional, physical, and spiritual human needs.
- By promoting human care, the theory reinforces patient dignity, ensuring the nursing profession delivers compassionate and ethical care.
- This approach elevates the quality of nursing care, aligning with the science of caring as an essential part of professional nursing.
B. Emphasis on the Caring Process and Caring Behaviors
- The theory emphasizes the care process, where caring behaviors such as empathy, presence, and respect are integrated into nursing practice.
- Through caritas and caritas processes, nurses are guided to demonstrate authentic caring in nursing.
- The focus on transpersonal caring ensures that every caring relationship becomes a healing encounter.
- These elements make the human caring theory a cornerstone of modern nursing theories.
C. Contribution to the Development of a Caring Model in Nursing
- Watson created a caring theory that provides a structured model for education, research, and clinical practice.
- The Watson Caring Science Institute continues to expand this caring model, supporting nurses worldwide in adopting holistic care practices.
- By integrating Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring, the nursing profession benefits from a framework that blends compassion with evidence-based practice.
- This contribution ensures that caring in nursing remains central to the growth of professional nursing and the future of healthcare.
The strengths of Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring lie in its ability to preserve dignity, emphasize caring behaviors, and provide a model that strengthens the nursing profession through compassion and the science of caring.
VII. Weaknesses of Watson’s Theory of Human Caring
A. Critiques and Limitations in Application
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring is widely respected; however, critics note challenges in consistently applying it across diverse healthcare environments.
- The theory of transpersonal caring requires time, presence, and emotional investment, which may not always be possible in busy hospital settings.
- Some argue that the caring science theory focuses heavily on philosophy rather than practical, measurable interventions.
- According to Watson, caring is central to nursing practice, yet the science and technology demands of modern healthcare sometimes overshadow this vision.
B. Challenges in Measuring the Impact of Caring Practices
- A limitation of Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring lies in the difficulty of measuring the outcomes of caring for patients and caring for others.
- The art and science of care, as emphasized in Watson’s caring theory, values compassion, dignity, and human connection, but these aspects are not easily quantifiable.
- Watson defines caring as the essence of nursing, yet translating this into measurable evidence in nursing education and practice remains complex.
- While studies in the Journal of Caring Sciences highlight benefits, the lack of standardized tools makes evaluation difficult.
C. Potential for Misinterpretation of the Theory
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring can be misinterpreted if taken as purely emotional rather than both art and science.
- Some may confuse Watson’s nursing theory with spiritual care alone, overlooking its balance of the science of unitary human and the model of human needs.
- Misuse of concepts like Watson Caritas or the caring environment may dilute the theory’s emphasis on the importance of holistic healing.
- Critics in nursing literature suggest that without clear guidelines, the future of nursing risks inconsistent application of Jean Watson’s caring science.
While Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring enriches the nursing science, its weaknesses include practical limitations, challenges in outcome measurement, and potential misinterpretation. Yet, despite these, it remains a cornerstone of Watson’s caring vision that continues to shape quality nursing care.
VIII. Additional Key Concepts for Nursing Students
A. Caritas Processes and Their Significance
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring introduces the caritas processes as guiding principles in nursing approaches.
- These processes emphasize caring and love, presence, and empathy in addressing the centrality of human needs.
- For nursing students, understanding caritas highlights that the theory of caring is both complementary to the science and central to the concept in nursing.
- Watson contends that caring cannot be separated from healing, making caritas essential to health nursing and psychiatric and mental health nursing.
B. Transpersonal Caring Relationships and Caring Consciousness
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring emphasizes transpersonal caring relationships, in which nurses connect with patients on a deeper level beyond physical care.
- This approach supports caring and the one, creating a healing encounter rooted in presence and caring consciousness.
- Such relationships demonstrate that caring is not just task-oriented, but also spiritual, emotional, and deeply human.
- Nursing students learn that these connections respect human dignity and uphold the essence of nursing in professional practice.
C. The Actual Caring Occasion in Nursing Practice
- The actual caring occasion is a core idea in Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring, where the nurse and patient meet in an authentic moment of care.
- This concept in nursing suggests that healing occurs not only through treatment but also through shared experiences.
- Students are taught to recognize these moments in nursing practice, especially in complex areas like psychiatric and mental health nursing.
- Such occasions remind nurses that the theory of caring places equal value on the art and science of healthcare.
D. Connection to the Watson Caring Science Institute
- The Watson Caring Science Institute expands human caring at the university level and beyond, offering programs for nursing education and practice.
- Founded by Jean Watson, a distinguished professor of nursing, the institute promotes the global application of her theory of caring.
- Watson, recognized by the American Academy of Nursing and honored with the Visionary Award for Caring Science and the Award for Caring Science Leadership, continues to influence the future of nursing.
- Her career milestones, from her early education at the Lewis Gale School of Nursing in Roanoke to recognition by the Academy of Nursing in 2013, prove her lasting impact.
- Nursing students are reminded that Jean Watson was born as Margaret Jean Harmon and has been in nursing since 1964, before she began developing her theory to ensure caring in nursing remains at the heart of the profession.
For students, the key concepts of Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring—caritas processes, transpersonal caring, and the actual caring occasion—illustrate how nursing theorist Jean Watson redefined the theory of caring. Through the Watson Caring Science Institute, her work continues to shape nursing education and practice, ensuring that caring in nursing remains the foundation of the nursing profession.
IX. Conclusion
Summary of the Theory’s Impact
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring remains one of the most influential frameworks in modern nursing.
- Watson began developing her theory to highlight that the theory of caring is both an art and a science within the nursing profession.
- The theory emphasizes caring behaviors, including empathy, respect, and presence, which are essential in nursing education and practice.
Relevance to Nursing and Healthcare
- Through its focus on caring practices, the theory shows that health nursing must integrate compassion alongside medical knowledge.
- Watson’s caring philosophy insists that healing is not just technical but deeply human, shaped by authentic nurse–patient relationships.
- By connecting the art and science of nursing, the model ensures that dignity and holistic care are preserved in practice.
Final Reflection
- Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring inspires nurses to see their role as healers who embody compassion and respect.
- Its legacy continues to transform caring practices, advancing a vision where nursing education and practice prepare professionals to meet human needs with both skill and love.
- Ultimately, Watson’s caring reminds us that the theory of caring is the true essence of nursing.
X. FAQs: Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring
What are the main points of Jean Watson’s theory?
- Holistic focus: Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring frames the theory of caring as the union of art and science, honoring body–mind–spirit.
- Transpersonal relationship: Healing arises through authentic connection and presence (core to Watson’s caring).
- Caritas processes: Ten value-guided caring behaviors that operationalize compassion in care.
- Historical note: As sources recount, “Watson began developing her theory” in the 1970s to re-center caring within nursing.
What are the applications of Watson’s Theory of Human Caring?
- Clinical settings: Guides caring practices in acute, community, and health nursing environments.
- Nursing education and practice: Curricula embed caritas for reflective, person-centered care.
- Leadership & culture: Shapes caring workplaces and staff well-being.
- Quality & outcomes: Aligns documentation, safety, and satisfaction with caring metrics.
How is Jean Watson’s theory used today?
- Care plans: Teams apply Caritas to assessment, planning, and evaluation—showing how Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring translates into daily workflows.
- Reflective practice: Nurses journal, debrief, and cultivate presence to strengthen caring behaviors.
- Inter-professional care: Shared language for empathy and collaboration in complex cases.
- Patient experience: Jean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring informs initiatives that elevate dignity and trust.
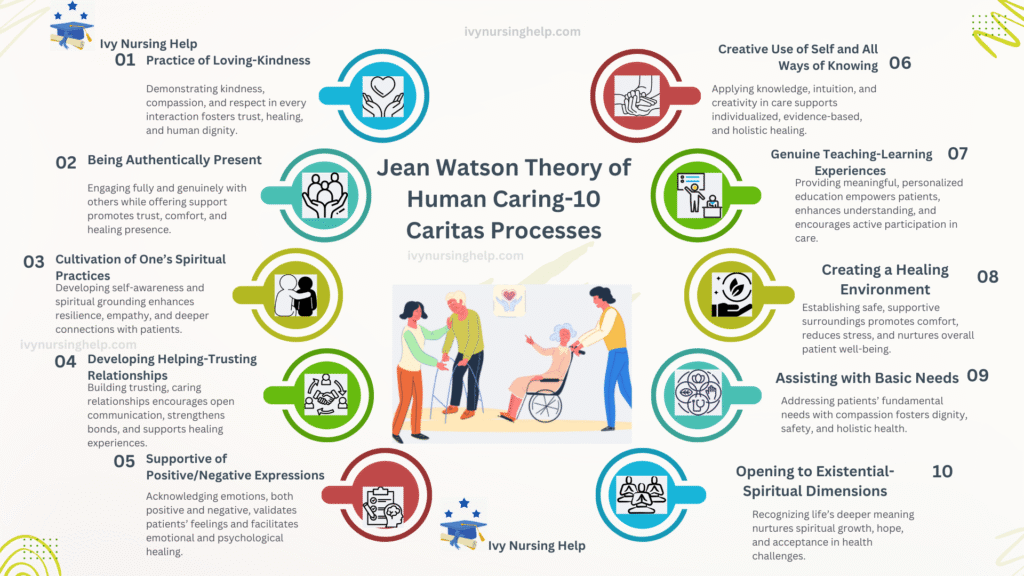
What are the 10 carative factors in Jean Watson’s theory of human caring?
- Often taught as Caritas Processes that are complementary to science:
- Loving-kindness; Faith–hope; Sensitivity to self/others; Helping–trusting relationship; Expression of feelings; Creative problem-solving/caring process; Teaching–learning; Supportive environment; Human needs assistance; Spiritual–existential care.
- For students, these summarize howJean Watson’s Theory of Human Caring becomes practical, testable habits across nursing education and practice and clinical care.
The framework centers human dignity and guides compassionate, evidence-aligned care across health nursing, education, and leadership—keeping caring at the heart of professional nursing.
