Nursing Theories
I. Introduction
Definition of Nursing
- Nursing is a healthcare profession focused on nursing care, promoting health, preventing illness, and supporting recovery.
- It involves patient care through assessment, nursing intervention, and evaluation to meet physical, emotional, and social needs.
- The nursing profession draws on nursing knowledge built over time by nursing theorist contributions, including grand nursing theories, middle-range nursing theories, and specific models like the self-care deficit theory and theory of comfort.
B. Importance of Nursing Theories in the Nursing Profession
- Nursing theories provide a foundation for nursing practice, guiding how nurses deliver patient care in different settings.
- These theories guide assessment, planning, and delivery of nursing care, ensuring evidence-based and consistent approaches.
- The theories link nursing research, nursing education, and clinical practice, strengthening the model of nursing.
- They help nurses apply nursing metaparadigm concepts—person, health, environment, and nursing—within modern nursing frameworks.
- Theories such as the theory of interpersonal relations, need theory, and transcultural nursing enhance cultural sensitivity, communication, and holistic patient care.
C. Overview of the Article
- This article will:
- Explore grand theories that define the scope of the nursing profession.
- Examine middle-range theories for practical, everyday nursing problems.
- Discuss care theory and specific nursing frameworks like the self-care deficit theory.
- Highlight how nursing theories support nursing students in understanding theory in nursing and applying it to nursing practice.
Key Points Covered in the Article:
- Nursing theories form the scientific basis for nursing care and nursing intervention.
- Grand nursing theories address broad perspectives, while middle-range nursing theories focus on targeted aspects of care.
- Nursing theories provide structured ways to help nurses improve patient care outcomes.
- Models such as the model of nursing and care theory connect academic concepts to clinical practice.
- Nursing research tests and refines nursing theories, ensuring they remain relevant to modern nursing.
- Theories may evolve over time to address new nursing problems and improve nursing education strategies.
- Understanding these theories empowers nursing students and practicing nurses to deliver safe, effective, and culturally appropriate care.
II. Foundations of Nursing Theories
A. Historical Context and Development of Nursing Theory
- Nursing theories originated to define the nursing profession as a distinct discipline separate from medicine.
- Early nursing theories were influenced by pioneers like Florence Nightingale, who emphasized environment and nursing care.
- The mid-20th century saw the formalization of theory in nursing to support structured nursing practice, nursing education, and nursing research.
- The development of grand nursing theories, middle-range nursing theories, and specific nursing models aimed to help nurses address diverse nursing problems in modern nursing.
- Over time, the theories provide a strong foundation for consistent patient care and nursing intervention across settings.
B. Key Nursing Theorists and Their Contributions
- Nursing theorist Hildegard Peplau – Theory of Interpersonal Relations: Theory focuses on nurse-patient relationships to improve patient care outcomes.
- Dorothea Orem – Self-Care Deficit Theory: Care theory designed to help nurses support patient independence.
- Virginia Henderson – Need Theory: Guides nursing practice by identifying basic human needs.
- Madeleine Leininger – Transcultural Nursing: Integrates cultural values into nursing care.
- Katharine Kolcaba – Theory of Comfort: Addresses physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being.
- Each nursing model developed by these theorists shaped nursing knowledge, nursing education, and clinical practice worldwide.
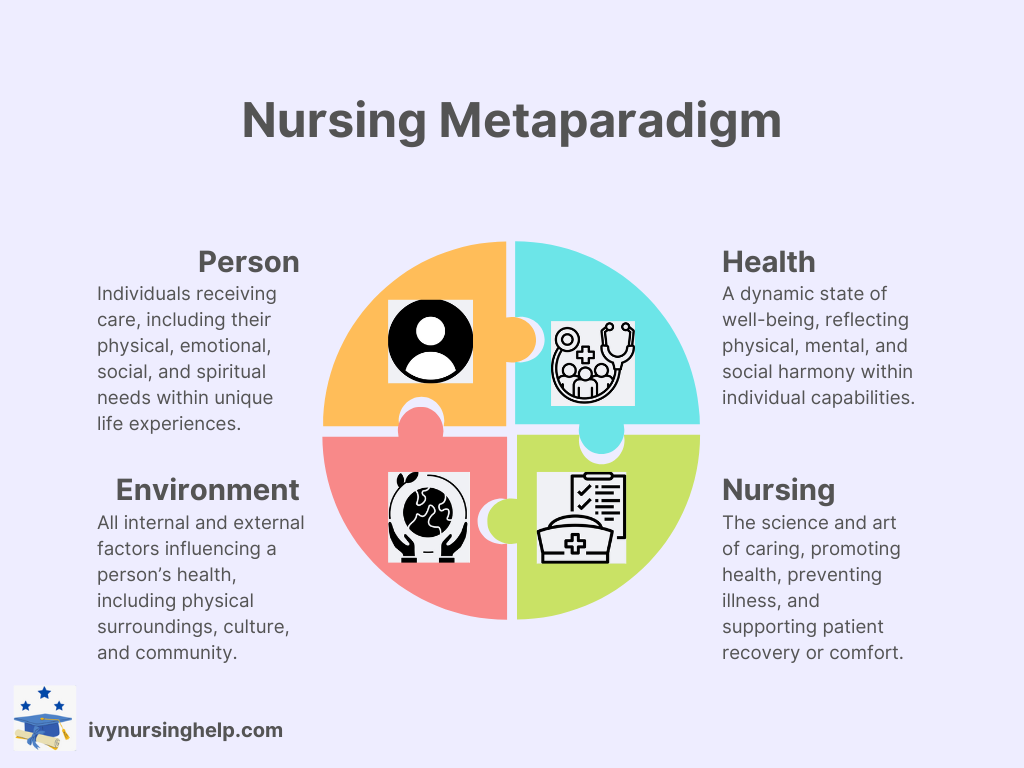
C. Overview of the Nursing Metaparadigm
- The nursing metaparadigm includes four central concepts:
- Person – the recipient of nursing care.
- Health – overall well-being and quality of life.
- Environment – all external conditions affecting health.
- Nursing – the actions and responsibilities of the nursing profession.
- Theories guide how these elements interact in nursing practice and the model of nursing frameworks.
- Theories may adapt over time to reflect evolving nursing problems and healthcare needs.
D. Types of Nursing Theories
- Grand Nursing Theories – Broad frameworks that explain the overall nature of nursing practice (e.g., Orem’s Self-Care Deficit Theory).
- Middle-Range Nursing Theories – More focused, practical applications for nursing intervention (e.g., Kolcaba’s Theory of Comfort).
- Middle-range theories address specific areas of nursing care without being overly abstract.
- Specific Nursing Models – Target unique clinical or cultural contexts, such as Transcultural Nursing.
- These theories provide a roadmap for nursing students, educators, and practitioners to integrate nursing knowledge into patient care effectively.
III. Grand Nursing Theories
Definition and Characteristics
- Grand nursing theories are broad, abstract frameworks that define the overall scope of nursing practice.
- They provide general principles for nursing care, nursing intervention, and patient care without focusing on specific conditions.
- Developed by influential nursing theorist pioneers, nursing theories provide a conceptual base for the nursing profession, nursing education, and nursing research.
- Theories guide the application of the nursing metaparadigm (person, health, environment, nursing) in diverse clinical practice settings.
- Grand theories are essential for shaping modern nursing and developing more focused middle-range theories.
B. Major Grand Theories
- Self-Care Deficit Theory – Dorothea Orem’s care theory is designed to help nurses promote patient independence.
- Theory of Interpersonal Relations – Hildegard Peplau’s theory focuses on therapeutic nurse-patient communication to improve outcomes.
- Need Theory – Virginia Henderson’s model of nursing that identifies essential needs for health and recovery.
- Transcultural Nursing – Madeleine Leininger’s specific nursing model that addresses cultural diversity in patient care.
- Theory of Comfort – Katharine Kolcaba’s holistic approach to nursing care, focusing on relief, ease, and transcendence.
C. Theory of Nursing Systems
- Originates from Orem’s Self-Care Deficit Theory and expands into three nurse theories of care:
- Wholly compensatory – Nurse provides all nursing intervention when the patient cannot self-care.
- Partly compensatory – Nurse supports patient efforts while encouraging independence.
- Supportive-educative – Nurse provides nursing education and guidance for self-management.
- This nursing model applies across the nursing profession to address various nursing problems and maintain quality patient care.
D. Theory of Health as Expanding
- Margaret Newman’s theory in nursing suggests health is not merely the absence of disease but a process of expanding consciousness.
- Theories may redefine illness as part of personal growth and human potential.
- Aligns with the nursing metaparadigm by integrating person, environment, and health into nursing practice.
- Encourages nursing students and practitioners to focus on life patterns rather than isolated symptoms.
- Serves as a philosophical foundation for nursing knowledge, influencing nursing research and clinical practice.
IV. Middle-Range Nursing Theories
A. Definition and Significance
- Middle-range nursing theories bridge the gap between grand nursing theories and day-to-day nursing practice.
- These theories are more specific, focusing on particular aspects of nursing care while still being broad enough for application in varied clinical practice settings.
- They provide practical guidance to help nurses solve real-world nursing problems through targeted nursing intervention.
- Developed by expert nursing theorist leaders, they link nursing research, nursing education, and the nursing profession into a unified model of nursing.
- Theories guide the use of the nursing metaparadigm—person, health, environment, and nursing—at a more operational level.
B. Key Middle-Range Theories
- Often derived from grand theories but adapted for more specific nursing care applications.
- Examples include:
- Self-Care Deficit Theory – focuses on patient independence.
- Theory of Goal Attainment – emphasizes collaborative care.
- Theory of Comfort – centers on holistic well-being.
- Transcultural Nursing Theory – integrates cultural competence.
- Middle-range theories provide frameworks for improving patient care across different nursing model contexts.
C. Self-Care Deficit Theory
- Created by Dorothea Orem, a renowned nursing theorist.
- Care theory focuses on helping patients perform self-care when they cannot do so independently.
- Divided into wholly compensatory, partly compensatory, and supportive-educative systems.
- Widely used in nursing education, nursing practice, and modern nursing to enhance independence.
D. Theory of Goal Attainment
- Developed by Imogene King to improve nursing practice through shared decision-making.
- Encourages mutual goal setting between nurse and patient for better patient care outcomes.
- The theory may be applied in acute care, rehabilitation, and community health.
E. Theory of Comfort
- Introduced by Katharine Kolcaba to address the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of patients.
- Integrates into theory in nursing to improve recovery, especially in palliative care and chronic illness management.
F. Transcultural Nursing Theory
- Developed by Madeleine Leininger to ensure nursing care respects cultural values and beliefs.
- Specific nursing approach to increase trust, compliance, and satisfaction.
- Applied in nursing research and clinical practice to address diversity-related nursing problems.
V. Application of Nursing Theories in Nursing Practice
A. Role of Nursing Theories in Clinical Practice
- Nursing theories form the foundation of nursing practice, ensuring care is systematic and evidence-based.
- These theories link nursing knowledge to nursing care, enabling a consistent approach to patient care.
- Both grand nursing theories and middle-range theories influence how nurses assess, plan, implement, and evaluate care.
- They provide a framework for applying the nursing metaparadigm—person, health, environment, and nursing—in everyday clinical practice.
- Nursing theorist contributions, such as the self-care deficit theory, theory of interpersonal relations, and need theory, remain vital in modern nursing.
B. Nursing Interventions Based on Theory
- Nursing intervention is planned and implemented based on principles from nursing theories.
- Care theory from the model of nursing guides how nurses deliver individualized treatment.
- Specific nursing models like transcultural nursing address cultural diversity in interventions.
- The theory of comfort enhances holistic care, focusing on emotional, physical, and spiritual well-being.
- Theories guide interventions that improve outcomes, reduce nursing problems, and strengthen the nursing profession.
C. Theories Guide Patient Care and Nursing Problems
- Middle-range theories focus on solving nursing problems within targeted patient populations.
- Grand theories provide the overall vision, while middle-range theories translate them into actionable steps.
- Theory in nursing ensures that every aspect of nursing care—from prevention to rehabilitation—is structured.
- Nursing research validates these approaches and integrates new findings into nursing education for nursing students.
- Theories may evolve to adapt to emerging challenges in healthcare and clinical practice.
D. Gap Between Theory and Practice
- Despite their importance, there can be a gap between nursing theories and real-world applications.
- Time constraints, resource limitations, and varying nursing model implementations can affect theory integration.
- Bridging this gap requires:
- Stronger links between nursing education and practice settings.
- Ongoing nursing research to refine existing theories.
- Encouraging nursing students and professionals to apply theory consistently in modern nursing.
- When applied effectively, nursing theories help nurses provide safe, culturally competent, and patient-centered care.
VI. Nursing Education and Theoretical Frameworks
A. Importance of Nursing Theories in Nursing Education
- Nursing theories are essential in nursing education, providing the foundation for nursing practice and the advancement of the nursing profession.
- Nursing theories play a vital role in linking nursing philosophies, nursing ideas, and nursing research into cohesive learning structures.
- Theories provide frameworks for nursing interventions, ensuring nursing students understand the rationale behind care decisions.
- From Florence Nightingale’s environmental theory to Peplau’s theory of interpersonal relations, these concepts help define the field of nursing and enhance the understanding of nursing.
- Nursing theories guide curriculum development in programs such as the Master of Science in Nursing.
B. Preparing Nursing Students with Theoretical Knowledge
- Nursing practice is based on theoretical knowledge that supports evidence-based care.
- Exposure to the list of nursing theories, including nursing need theory, self-care deficit nursing theory, and the 21 nursing problems, equips students with diverse approaches to receiving nursing care.
- Middle-range nursing theories are narrower than grand theories, making them ideal for teaching practice-level nursing theories that address specific care situations.
- The nursing process—assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation—is linked to theory for better outcomes.
- Theories and models like the system model of nursing help nursing students integrate components of the nursing metaparadigm into modern nursing contexts.
C. Frameworks for Nurses in Modern Nursing
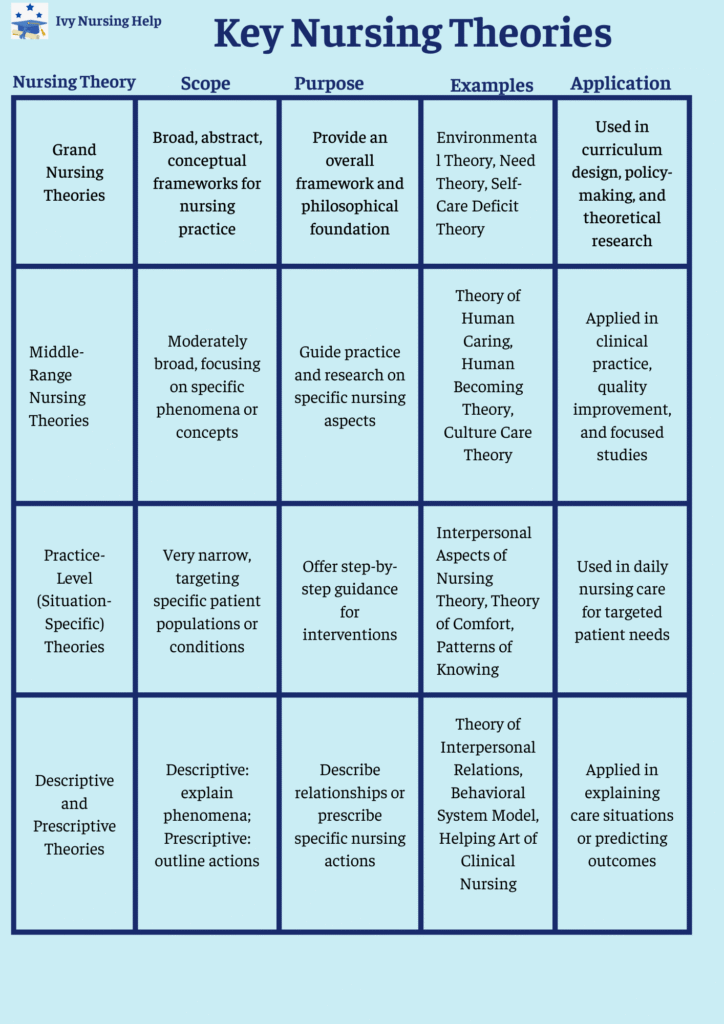
- Theories fall under three main categories: grand nursing theories, middle-range theory, and practice-level nursing theories provide focused guidance for daily tasks.
- Theories provide frameworks for nursing that connect nursing research and create practical guidelines for clinical application.
- The theory of self-care and self-care deficit nursing theory emphasises independence and patient empowerment.
- Theory identifies key concepts such as patient needs, cultural context, and health environment for individualized care.
- Peplau’s theory of interpersonal relations describes how communication and trust enhance nursing career satisfaction and patient care quality.
- Theory suggests that patients benefit when care is aligned with their personal and cultural needs, reinforcing the purpose of nursing theories and nursing as a discipline.
VII. Nursing Research and Theoretical Work
A. Advances in Nursing Science
- Nursing theories have significantly contributed to the advancement of the nursing profession and the growth of nursing science.
- The first nursing frameworks, such as Florence Nightingale’s environmental theory, established the foundation for evidence-based practice.
- Publications like Nursing Science Quarterly share innovations and research guided by nursing philosophies, theories, and models.
- Nursing theories are important for shaping new care models, enhancing the understanding of nursing, and improving the field of nursing.
- These theories fall under three categories: grand theories, middle-range theories, and practice-level theories, which provide targeted applications for research.
B. Nursing Research Informed by Theories
- Nursing practice is based on theoretical frameworks that nursing theories provide for structured investigation.
- Nursing research creates new approaches to nursing care, drawing from established models like the system model of nursing and the theory of self-care.
- The nursing process—assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, evaluation—is often tested and refined through research aligned with nursing theories.
- Self-care deficit nursing theory, nursing need theory, and Peplau’s theory of interpersonal relations guide research into patient autonomy, needs, and communication.
- Studies compare concepts compared to grand theories, or middle-range theories, that define the aspect for practical use in nursing career development.
Power Up Your Nursing Assignment Success
Ace your nursing assignments with IvyNursingHelp.com! Our expert nursing writers deliver well-researched, plagiarism-free work on time—every time. Get personalized assistance tailored to your academic needs. Click now and secure top grades with professional support!
C. Theoretical Work in Nursing and Its Impact
- Nursing theories guide and define nursing concepts, providing frameworks for nursing interventions that can be tested and adapted to different settings.
- Theory identifies core components of the nursing metaparadigm—person, health, environment, and nursing—ensuring a unified approach.
- Research on 21 nursing problems validates strategies for receiving nursing care in diverse populations.
- Theory describes how patients’ needs evolve, and theory suggests that patients benefit from culturally sensitive care.
- Nursing theories and nursing research together support curriculum design in the Master of Science in Nursing programs.
- These theories play a vital role in connecting nursing ideas with evidence-based outcomes, ensuring that theories play a vital role in both practice and policy-making.
- Middle-range nursing theories are narrower but highly effective in translating research into clinical improvements.
VIII. Caring in Nursing
A. The Role of Caring in Nursing
- Caring is central to the field of nursing and a core concept in many nursing theories.
- Nursing practice is based on compassion, empathy, and respect for patients, supported by nursing philosophies, theories, and models.
- Early frameworks, such as Florence Nightingale’s environmental theory and the first nursing principles, emphasized the nurse’s role in creating a healing environment.
- Nursing theories play a vital role in defining and sustaining caring behaviors across the nursing career.
- The nursing process ensures caring is embedded in assessment, planning, receiving nursing care, and evaluation.
- Nursing theories are important for ensuring that caring is not only an attitude but also a structured, evidence-based practice.
B. Theories That Focus on Care
- Peplau’s theory of interpersonal relations – The theory describes how building trust and communication enhances caring in nursing theories and nursing practice.
- Nursing need theory – Identifies fundamental patient needs and the nurse’s responsibility in meeting them.
- Theory of self-care and self-care deficit nursing theory – Focus on empowering patients to maintain independence, while the theory suggests that patients may require different levels of assistance.
- System model of nursing – Offers a structured way to integrate caring with other components of the nursing metaparadigm.
- 21 nursing problems model – Uses problem-solving to prioritize care in practice-level nursing theories, and provide applications.
- The list of nursing theories includes many care-focused frameworks, each with its own nursing ideas and strategies.
C. Importance of Nursing Knowledge in Delivering Care
- Nursing theories guide the development of knowledge that supports effective caring practices.
- Theories provide frameworks for nursing interventions by integrating compassion with nursing research and creating evidence-based approaches.
- Middle-range theory defines the aspect of care delivery, making it more specific than grand theories but still widely applicable.
- Nursing theories play a key role in the advancement of the nursing profession through ongoing education, such as the Master of Science in Nursing programs.
- Theories play a vital role in connecting caring behaviors with measurable patient outcomes.
- Nurses and educators use caring-focused nursing theories to improve the understanding of nursing and enhance patient satisfaction.
- Middle-range nursing theories are narrower, allowing focused application in specific care settings while still aligning with the broader goals of nursing theories.
IX. Conclusion
A. The Role of Caring in Nursing
- Caring is central to the field of nursing and a core concept in many nursing theories.
- Nursing practice is based on compassion, empathy, and respect for patients, supported by nursing philosophies, theories, and models.
- Early frameworks, such as Florence Nightingale’s environmental theory and the first nursing principles, emphasized the nurse’s role in creating a healing environment.
- Nursing theories play a vital role in defining and sustaining caring behaviors across the nursing career.
- The nursing process ensures caring is embedded in assessment, planning, receiving nursing care, and evaluation.
- Nursing theories are important for ensuring that caring is not only an attitude but also a structured, evidence-based practice.
B. Theories That Focus on Care
- Peplau’s theory of interpersonal relations – The theory describes how building trust and communication enhances caring in nursing theories and nursing practice.
- Nursing need theory – Identifies fundamental patient needs and the nurse’s responsibility in meeting them.
- Theory of self-care and self-care deficit nursing theory – Focus on empowering patients to maintain independence, while the theory suggests that patients may require different levels of assistance.
- System model of nursing – Offers a structured way to integrate caring with other components of the nursing metaparadigm.
- 21 nursing problems model – Uses problem-solving to prioritize care in practice-level nursing theories, providing applications.
- The list of nursing theories includes many care-focused frameworks, each with its unique nursing ideas and strategies.
C. Importance of Nursing Knowledge in Delivering Care
- Nursing theories guide the development of knowledge that supports effective caring practices.
- Theories provide frameworks for nursing interventions by integrating compassion with nursing research and creating evidence-based approaches.
- Middle-range theory defines the aspect of care delivery, making it more specific than grand theories but still widely applicable.
- Nursing theories play a key role in the advancement of the nursing profession through ongoing education, such as the Master of Science in Nursing programs.
- Theories play a vital role in connecting caring behaviors with measurable patient outcomes.
- Nurses and tutors utilize caring-focused nursing theories to improve the understanding of nursing and enhance patient satisfaction.
- Middle-range nursing theories are narrower, allowing focused application in specific care settings while still aligning with the broader goals of nursing theories.
FAQs: Nursing Theories
What are the 4 types of nursing theory?
- Nursing theories are generally classified into four types:
- Grand theories – Broad nursing philosophies offering comprehensive views of the field of nursing.
- Middle-range nursing theories – More specific; middle-range theory defines the aspect of care for targeted applications.
- Practice-level nursing theories– Provide direct guidance for daily nursing practice and receiving nursing care.
- Theories and models– Integrate elements from multiple categories, such as the system model of nursing.
- These theories guide how nurses apply the nursing process and align care with components of the nursing metaparadigm.
What are the 4 patient theories?
- Common patient-focused nursing theories include:
- Theory of self-care – Central toself-care deficit nursing theory, emphasizing patient independence.
- Nursing need theory – Identifies essential patient needs and the nurse’s role.
- Peplau’s theory of interpersonal relations – The theory describes therapeutic nurse-patient communication.
- 21 nursing problems – Theory identifies priority patient needs to enhance nursing career effectiveness.
- These theories provide frameworks for nursing interventions that address both physical and emotional needs.
What are the 4 nursing theories in community health nursing?
- Frequently used nursing theories in community health include:
- Environmental theory – Part of the first nursing frameworks, improving community health environments.
- Nursing need theory – Applied in public health outreach.
- Theory of self-care – Encourages community self-management of health.
- System model of nursing – Focuses on prevention and holistic care.
- These theories are important for shaping community programs and nursing research, and creating sustainable health strategies.
What are Florence Nightingale’s theories?
- Florence Nightingale’s environmental theory is one of the most recognized in the list of nursing theories.
- Theory suggests that patients recover better in clean, well-ventilated environments.
- Her work, published in Nursing Science Quarterly and historical texts, remains a foundation for nursing theories and nursing education.
- Nursing practice is based on her principles, influencing American nurses, global health policies, and the advancement of the nursing profession.
- Nursing theories play a vital role today by linking her nursing ideas with modern evidence-based care.
