Florence Nightingale’s Environmental Theory
I. Introduction
A. Overview of Florence Nightingale
- Florence Nightingale, known as the founder of modern nursing, made significant contributions during the Crimean War.
- As a nurse, she emphasized the connection between the physical environment and patient recovery.
- Her legacy includes the Nightingale Pledge, the foundation of nursing education, and her groundbreaking work, Notes on Nursing.
• B. Importance of Environmental Theory in Nursing
- Florence Nightingale’s Environmental Theory is a fundamental nursing theory that highlights how the environment for a patient affects health outcomes.
- It stresses aspects such as cleanliness, fresh air, light, proper nutrition, and noise control.
- This environmental theory revolutionized nursing practice and laid the foundation for modern infection control methods.
- The theory is still relevant today in promoting patient-centered nursing care.
- It influenced hospital design, public health, and nursing research around the world.
• C. Purpose of the Article
- The purpose of this article is to explore Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory and its enduring impact on nursing practice.
- It will examine how Florence Nightingale’s principles continue to guide modern nurses in ensuring optimal environments for healing.
- By revisiting Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory, we acknowledge the role of nursing theory in enhancing quality care and safety.
- This article also connects historical insights to current standards in nursing education and hospital management.
Key Elements of Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory
- Cleanliness: Nightingale stressed that a clean environment prevents the spread of disease and promotes healing.
- Ventilation: Fresh air was vital to recovery, and she advocated for proper airflow in patient areas.
- Light and Noise: Exposure to natural light and minimizing noise were essential for emotional and physical well-being.
- Nutrition: Proper food intake supported the healing process, making diet an integral part of nursing care.
- Infection Control: Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory introduced early ideas that form today’s infection control protocols.
Modern Applications
- Hospital Design: Layouts now consider light, noise, and airflow—principles rooted in Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory.
- Patient Safety: Environmental checks and protocols are part of modern nursing practice.
- Nursing Education: Courses still teach Florence Nightingale’s contributions and emphasize environmental factors.
- Nursing Research: Studies continue to support her theory, showing how the environment impacts patient outcomes.
- Global Influence: Her theory shapes care delivery beyond the hospital, especially in home health and public settings.
- Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory remains one of the most influential theories in nursing, reinforcing the need to maintain a therapeutic environment for healing and holistic care.
II. Historical Context
A. Florence Nightingale and the Crimean War
- Florence Nightingale rose to prominence as a nurse during the Crimean War, where she managed and improved battlefield hospitals.
- She witnessed firsthand the dire effects of a poor physical environment on the wounded soldiers’ health and recovery.
- This experience formed the foundation of Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory, as she sought to transform hospital conditions through practical changes.
- Nightingale’s efforts drastically reduced mortality rates, reinforcing the importance of clean surroundings in nursing care.
- Her wartime observations became the basis for her later work, Notes on Nursing, which remains a cornerstone in nursing education.
B. Development of Nightingale’s Environmental Theory
- After returning from the Crimean War, Florence Nightingale formalized her insights into a structured nursing theory.
- Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory emphasized the need for a clean, quiet, and well-ventilated environment for the patient.
- She identified key environmental factors—such as fresh air, pure water, efficient drainage, cleanliness, and light—that influence health outcomes.
- Her belief that nature could assist in healing patients marked a revolutionary shift in nursing practice at the time.
- Nightingale advocated for these principles in hospital reforms, influencing global health care practices.
C. Influence of Germ Theory on Nightingale’s Work
- Though Florence Nightingale developed her environmental theory before germ theory was widely accepted, her ideas strongly aligned with later discoveries about microorganisms.
- The rise of infection control protocols in medicine validated the preventative aspects of Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory.
- She believed that controlling the physical environment could limit disease spread, which echoed the principles of modern germ theory.
- While Nightingale did not fully endorse germ theory initially, her emphasis on hygiene and sanitation made her a pioneer in practical disease prevention.
- Her teachings laid the groundwork for modern nursing research focused on environmental factors and their effects on health.
- Today, Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory continues to guide nursing education, nursing practice, and hospital design standards.
- The Nightingale Pledge, still recited by nurses, honors her legacy in ethical nursing care and commitment to health improvement.
- From her experience in the Crimean War to her foundational nursing theory, Florence Nightingale remains a symbol of excellence and innovation in health care.
III. Key Components of Nightingale’s Environmental Theory
A. Aspects of the Environment
- Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory outlines specific aspects of the environment that directly affect healing.
- As a pioneering nurse, Florence Nightingale believed that modifying the environment for the patient could greatly enhance recovery.
- Her nursing theory emphasizes cleanliness, light, ventilation, noise control, and nutrition.
- These elements form the core of effective nursing care and remain central in today’s nursing practice.
- Nightingale’s focus on both physical and emotional factors sets the foundation for holistic care in nursing education and application.
B. Physical Environment
- According to Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory, the physical environment plays a crucial role in patient outcomes.
- Cleanliness was paramount—dirty surroundings were linked to illness during the Crimean War, inspiring Nightingale’s sanitation reforms.
- Adequate ventilation ensured fresh air circulation, reducing the buildup of harmful pathogens.
- Proper lighting, especially natural light, was seen as beneficial for both physical and mental well-being.
- These practices contributed significantly to early infection control efforts and laid the groundwork for modern hospital design.
C. Psychological Environment
- Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory also addresses the psychological environment, showing her deep understanding of emotional well-being.
- Nightingale believed that a quiet, orderly, and compassionate setting positively influenced recovery.
- She advocated for minimizing noise and stress around patients to reduce anxiety and promote rest.
- Her attention to emotional health showed her commitment to holistic nursing care, going beyond physical treatment.
- These principles are still taught innursing education programs and applied in everyday nursing practice.
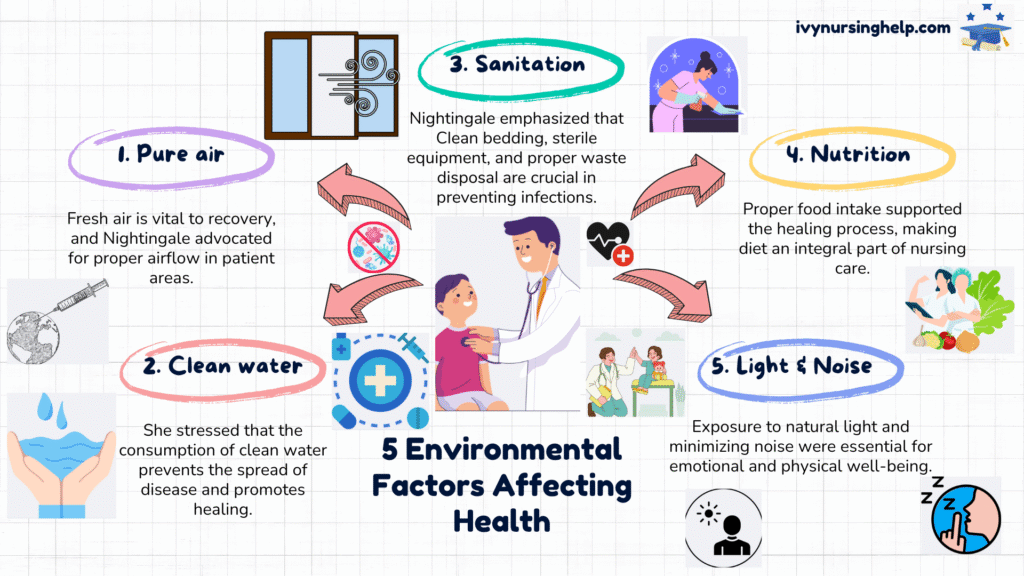
D. Environmental Factors Affecting Health
- Florence’s Nightingale Environmental Theoryidentifies multiple environmental factors that can impact a patient’s health, including:
- Sanitation: Clean bedding, sterile equipment, and waste disposal prevent infections.
- Light and Air: Vital for healing and reducing the risk of airborne diseases.
- Noise: Must be controlled to allow patient rest.
- Nutrition: Essential for recovery, monitored and managed by the nurse.
- Nightingale’s ideas, shared in her Notes on Nursing, shaped nursing research and practice worldwide.
- Her environmental theory continues to influence healthcare facilities, aligning with the ethical standards outlined in the Nightingale Pledge.
- Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory remains a foundational pillar of nursing theory, driving high standards in nursing care, hospital environments, and nursing education across the globe.
IV. Application of Nightingale’s Environmental Theory
A. Nursing Practice
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory is central to the nursing process, guiding nurses to create conditions that allow nature to act in healing.
- Nightingale emphasized that nursing is different from medicine, focusing on environmental adjustments rather than direct medical treatment.
- In nursing practice, her approach ensures the environment of the patient remains clean, well-lit, and ventilated for optimal recovery.
- The theory empowers nurses to take proactive nursing actions in controlling air quality, noise, and hygiene.
- These principles still influence current nursing settings, from hospitals to community care.
B. Nursing Care and Infection Control
- Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory is a key framework for infection control, especially in reducing preventable illnesses.
- As stated in her nursing notes, the cleanliness of the environment directly impacts the risk of infection.
- She proved that a safe environment could lower mortality rates, even though some critics accused Nightingale of increasing the mortality rates early in her career—a claim addressed in Nightingale’s defence.
- The theory demonstrates that the physical environment consists of elements like clean bedding, fresh air, and proper waste disposal to limit contamination.
- Her ideas continue to shape the treatment of infection and disease protocols in nursing practice today.
C. Examples of Nightingale’s Nursing Concepts
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory is illustrated in Notes on Nursing, which provides further examples of Nightingale’s environmental principles.
- Concepts include controlling light and noise, ensuring consumption of pure water, and keeping rooms odor-free to support healing.
- She taught that the goal of nursing is to place patients in conditions where nature’s tendency to act can occur.
- Nursing notes that nursing should always protect patient comfort, safety, and dignity.
- These examples prove that the environment relates directly to disease, making environmental management a non-negotiable aspect of care.
D. Nursing Education and Training
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory remains integral to nursing education, shaping curricula since the days it was perceived as a female nursing establishment.
- Students learn that nursing is different from medicine, with a focus on environmental interventions rather than only treatments.
- Training emphasizes that the physical environment consists of components—light, air, cleanliness—that influence recovery.
- Modern programs still reflect the principles of nursing training Nightingale promoted, ensuring a long as a safe environment is maintained for all patients.
- This theory continues to inspire nursing process application and best practices in healthcare worldwide.
Power Up Your Nursing Success Online
Master your online nursing coursework with Ivy Nursing Help. Our expert tutors provide personalized guidance, ensuring you excel in every assignment. Get the academic edge you need—start your journey to nursing success today!
V. Nightingale’s Contributions to Nursing Theory
A. First Nursing Theorist
- Florence Nightingale’s Environmental Theory positioned her as the first nursing theorist in modern healthcare.
- She developed the theory of nursing that focused on the act of utilizing the environment to support healing.
- Her approach stated that theenvironment could be altered to enhance recovery, thus creating a model for nursing that endures to this day.
- Nightingale’s environment theory became a foundation for the nursing process, emphasizing assessment and environmental management.
- She asserted that “nursing is different from medicine,” marking a shift toward holistic nursing actions and patient-centered care.
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory clearly outlines how components of the physical environment—air, light, cleanliness, and noise—affect patient outcomes.
- This theory empowers the contemporary nursing profession to integrate environment-based care into modern practice.
- Her nursing concepts and their translation continue to influence current nursing education and bedside application.
- Principles of nursing training she introduced during nursing training in 1851 still guide classroom and clinical instruction worldwide.
B. Development of the Nightingale Pledge
- The Nightingale Pledge was inspired by Florence’s beliefs in ethics, duty, and professionalism in nursing.
- While not authored by her directly, it reflects the goal of nursing as a commitment to creating a healthy environment for patients.
- It reinforces her theory that nursing is to place the patient in the best condition for nature to act.
- The pledge represents the implications for nursing professionalism and highlights Nightingale’s long-standing influence on values upheld in nursing school curricula.
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory continues to shape the moral compass of modern nurses through this pledge.
C. Nightingale’s Notes on Nursing
- Her publication, Notes on Nursing, provides further examples of Nightingale’s deep understanding of health and the physical environment.
- She stated in her nursing notes that “cleanliness of environment relates directly to disease,” underscoring her belief in the control of the environment.
- Notes on Nursing discusses the environment of the patient and how to maintain health by controlling the environmental factors.
- These writings served as a guide for the female nursing establishment and the treatment of infection and disease in a time before modern antibiotics.
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory remains one of the most cited works in the subsequent development of her environmental legacy and translation into contemporary nursing practice.
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory is not just historical—it remains essential in the nursing practice therein, reinforcing that the physical environment consists of physical elements that must be managed to deliver excellent nursing care.
VI. Influence on Contemporary Nursing Practices
A. Impact on Modern Nursing
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory continues to shape the nursing process by emphasizing the act of utilizing the environment to support healing.
- It is clear that Nightingale envisioned a model for nursing where the environment of the patient is central to care.
- The environment could be altered to promote healing, which remains a foundational principle in current nursing standards.
- This theory in nursing practice encourages nurses to evaluate aspects of the physical environment, such as cleanliness, air quality, and noise levels.
- Her nursing concepts and their translation into today’s practice demonstrate how the goal of nursing remains aligned with her view: “nursing is to place the patient in the best condition for nature to act.”
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory also supports the idea that nursing is different from medicine, as it focuses on the control of the environment over direct treatment.
B. Nightingale’s Environmental Theory and Its Influence on Infection Control
- One of the most significant contributions of the Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory is its influence on contemporary infection control.
- Her observations during the Crimean War and later writings, like Notes on Nursing, stated in her nursing notes that “cleanliness of environment relates directly to health.”
- Nightingale proved that the environment relates directly to disease and advocated for managing components of the physical environment.
- By focusing on sanitation, ventilation, and hygiene, she laid the groundwork for modern treatment of infection and disease.
- Her nursing actions demonstrated that many infections could be prevented simply by maintaining and controlling the environmental factors.
- The development of her environmental theory is often cited in infection control policies taught in nursing school and implemented in clinical settings.
C. Application of Nightingale’s Theory in Nursing Research
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory continues to inspire nursing research that investigates the relationship between the physical environment and patient outcomes.
- Research exploring environmental aspects of her theory confirms the importance of temperature, light, and noise in recovery.
- Studies have shown that healing is accelerated in a healthy environment, supporting the translation into contemporary nursing practice.
- The implications for nursing are broad—hospitals today implement changes based on this Nightingale theory of nursing to improve care quality.
- The subsequent development of her environmental principles shows how her work still empowers the contemporary nursing profession.
- Through nursing training in 1851, Nightingale created a foundation that still informs how nurses are educated, how care is delivered, and how employment in nursing adapts to evolving health needs.
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory is not only historical—it remains a living, evolving framework guiding the nursing practice therein, from bedside care to public health and policy.
VII. Conclusion
A. Summary of Key Points
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory is a foundational theory of nursing that revolutionized modern healthcare.
- It emphasizes the act of utilizing the environment to aid recovery, a belief stated in her nursing notes and demonstrated during the Crimean War.
- The theory focuses on the environment of the patient, highlighting that the physical environment consists of physical elements that affect healing.
- Nightingale’s work clearly established that the cleanliness of the environment relates directly to outcomes and that the environment relates directly to disease.
- Through her model for nursing, Nightingale proved that the environment could be altered and maintained by controlling the environmental factors to ensure a healthy environment.
- This has long influenced the nursing process, education, and nursing practice therein.
B. Lasting Legacy of Florence Nightingale’s Environmental Theory
- The development of her environmental theory has had enduring implications for nursing, especially its influence on contemporary infection control.
- Nightingale, considered the first nursing theorist, shaped how we view hospital sanitation and the goal of nursing.
- The Nightingale theory of nursing redefined nursing actions as proactive, environment-focused efforts to improve patient well-being.
- Her teachings are reinforced every Nightingale’s Day, celebrated globally to honor her legacy.
- Notes on Nursing still provides further examples of Nightingale’s enduring principles, especially those connected to the physical environment and its role in care.
- The female nursing establishment, nursing training in 1851, and principles of nursing training all stem from her innovative approaches.
- Her theory empowers the contemporary nursing profession to apply environmental principles in clinical care and public health.
C. Future Directions in Nursing Practice and Education
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory continues to guide the translation into contemporary nursing practice.
- As nursing is different from medicine, Nightingale’s emphasis on environmental care offers distinct value in healthcare systems today.
- The subsequent development of her environmental principles has led to advanced nursing research, especially in the treatment of infection and disease through environmental design.
- Future nursing school programs will expand on her nursing concepts and their translation into global health systems.
- There is growing emphasis on the physical environment influence the social and emotional well-being of patients, aligning with her early teachings.
- As employment in nursing grows, Nightingale’s approach remains relevant in guiding current nursing trends and policies.
- It is clear that Nightingale laid the foundation for future innovations in care, keeping the Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory a central pillar in nursing’s evolution.
FAQs: Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory
What was Nightingale’s environmental theory?
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory is a foundational theory of nursing that emphasizes the act of utilizing the environment to aid healing.
- It states that the environment for patient care must be clean, well-ventilated, quiet, and sanitary to reduce suffering and promote recovery.
- As stated in her nursing notes, Nightingale believed the cleanliness of environment relates directly to patient outcomes.
- This model for nursing illustrates that nursing is to place the patient in the best condition for nature to act.
- Her ideas are still seen in current nursing, especially in the nursing process and environmental design in hospitals.
What was Florence Nightingale’s contribution to us?
- Florence Nightingale, considered the first nursing theorist, transformed healthcare with the development of her environmental theory during the Crimean War.
- Her Notes on Nursing laid the foundation for the principles of nursing training, still taught in nursing school today.
- She introduced sanitary reforms, reducing mortality and shaping the female nursing establishment.
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory remains relevant for its implications for nursing, influencing everything from nursing actions to hospital architecture.
- Her efforts also led to the translation into contemporary nursing practice, keeping the goal of nursing focused on a healthy environment.
What are the 5 environmental factors of Nightingale’s?
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory identifies five key components of the physical environment:
- Pure air – supports respiratory health.
- Clean water – prevents disease.
- Efficient drainage – controls waste and bacteria.
- Cleanliness – reduces infection risk.
- Light – especially sunlight, boosts mood and health.
- These environmental aspects of her theory show that the environment could be altered to treat illness.
- Nightingale taught that the physical environment, which then causes or prevents disease, is central to care.
- This understanding had a profound influence on contemporary infection control and continues to inform nursing practice therein.
What are the lessons of Nightingale’s environmental theory?
- The Florence Nightingale Environmental Theory teaches that the control of the environment is crucial in preventing illness and aiding recovery.
- Her theory empowers the contemporary nursing profession to focus on holistic care using nursing concepts and their translation into daily practice.
- It reminds nurses that nursing is different from medicine and centers on caring for the patient wholly.
- Nightingale’s environment theory serves as a reminder that even basic nursing actions like cleaning, airing rooms, and reducing noise contribute to healing.
- These lessons are evident in the subsequent development of her environmental influence on employment in nursing, nursing training in 1851, and beyond.
