PICOT Question Examples
1. Introduction
- Definition of PICOT
- PICOT is an acronym that guides the creation of a clear research question.
- P = Patient/Population, I = Intervention, C = Comparison, O = Outcome, T = Time.
- Using PICOT question examples helps students, nurses, and healthcare providers break down complex topics into focused research inquiries.
- Significance in Research
- A well-structured PICOT question makes it easier to conduct evidence-based studies.
- PICOT question examples provide direction, ensure precision, and strengthen clinical investigations.
- These structured questions improve the relevance and applicability of findings.
Importance of Formulating a PICOT Question for Evidence-Based Practice
- Guides Clinical Decision-Making
- PICOT question examples offer clarity when nurses and healthcare providers face uncertainties.
- They allow professionals to formulate inquiries that directly impact patient outcomes.
- Improves Evidence-Based Practice
- By relying on PICOT question examples, practitioners ensure that their research question is aligned with evidence-based practice.
- Example: In patients with diabetes, does lifestyle modification compared to medication alone improve long-term outcomes within six months?
- This shows how etiology, intervention, and outcomes can be studied effectively.
- Enhances Learning and Research Skills
- Students should use PICOT question examples to understand how to structure investigations.
- A strong research question framed with PICOT improves critical thinking and reduces common errors.
- Applicable Across Fields
- PICOT question examples are not limited to nursing but extend to public health, policy analysis, and education.
- For example, studying the etiology of childhood obesity using a PICOT question ensures precise outcomes.
- The PICO framework ensures questions remain specific and research-focused.
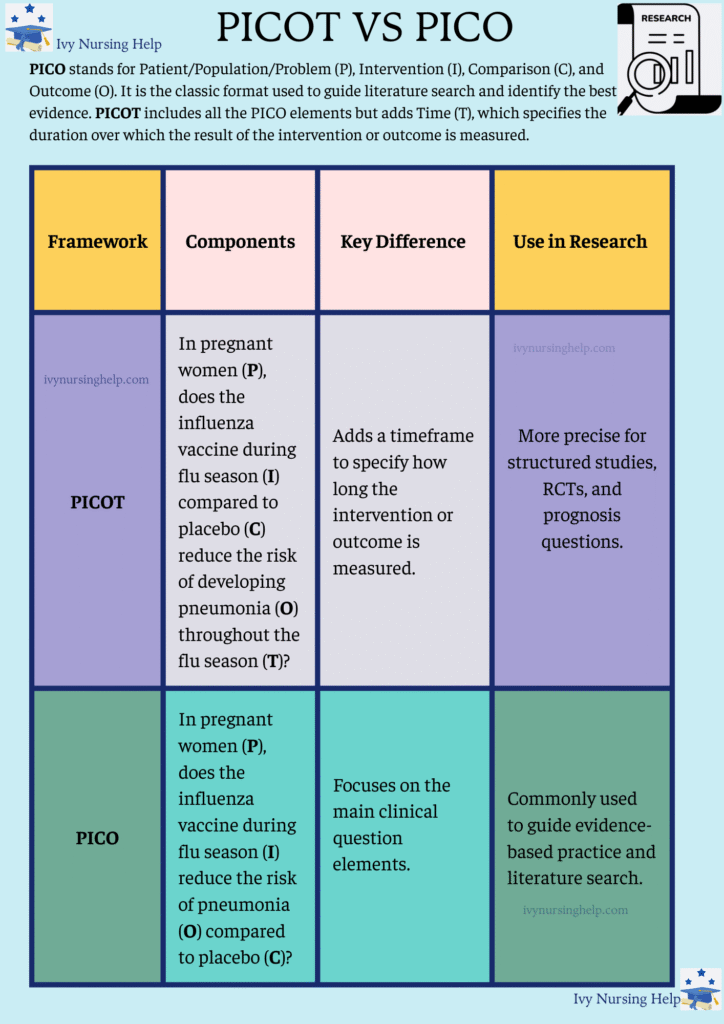
- PICO stands for Patient/Population/Problem (P), Intervention (I), Comparison (C), and Outcome (O). It is the classic format used to guide literature search and identify the best evidence.
- PICOT includes all the PICO elements but adds Time (T), which specifies the duration over which the result of the intervention or outcome is measured.
- PICO and PICOT are both frameworks used in evidence-based practice to structure a clear clinical question.
PICOT question examples are essential in nursing and healthcare research. They help formulate focused, evidence-based inquiries that drive clinical improvement. Whether addressing diabetes, patient safety, or other conditions, PICOT ensures a structured and impactful study design. PICO frames the essential elements of a clinical question, while PICOT enhances precision by including the timeframe, making it more useful for clinicians and researchers conducting structured studies.
2. Understanding the PICOT Framework
Understanding the PICOT Framework
- Explanation of the PICOT Acronym
- P – Population/Patient: Identifies the group being studied (e.g., adults with diabetes).
- I – Intervention: Refers to the treatment, practice, or program applied (e.g., lifestyle changes, new medication).
- C – Comparison: Explores alternatives to the intervention (e.g., medication alone, no treatment).
- O – Outcome: Defines the expected results (e.g., reduced blood sugar, improved health status).
- T – Time: Specifies the timeframe for measurement (e.g., six months, one year).
- Using PICOT question examples based on this framework ensures every research question is structured, measurable, and clinically relevant.
- How to Use the PICOT Framework to Develop Clinical Questions
- Step 1: Identify the Clinical Problem
- Nurses and healthcare providers begin by defining the issue, such as the etiology of a condition.
- Example: The high prevalence of type 2 diabetes in adult populations.
- Step 2: Formulate the Research Question
- Apply the acronym to formulate a precise PICOT question.
- Example: In adults with type 2 diabetes (P), does lifestyle modification (I) compared with medication alone (C) improve blood sugar control (O) within six months (T)?
- Reviewing PICOT question examples like this strengthens the ability to create focused, evidence-based questions.
- Step 3: Apply the PICO Logic
- The PICO structure ensures consistency and avoids vague or incomplete inquiries.
- Well-framed PICOT question examples are essential for systematic reviews, clinical guidelines, and nursing research.
- Step 4: Ensure Evidence-Based Relevance
- A good PICOT question connects directly to clinical practice, helping professionals make informed, evidence-based decisions.
- Example: In hospitalized patients (P), does frequent hand hygiene education (I) compared to routine instructions (C) reduce infection rates (O) over three months (T)?
- Step 5: Broaden Application
- PICOT question examples are not limited to nursing but also apply in public health, policy research, and preventive care.
- For instance, examining the etiology of childhood obesity can be structured into a research question using the PICOT format.
- Step 1: Identify the Clinical Problem
The PICOT framework is a reliable tool for structuring strong research questions. By practicing with multiple PICOT question examples, students and healthcare providers enhance their ability to formulate precise, evidence-based inquiries. Whether focusing on diabetes, infection prevention, or chronic illness, PICOT ensures clarity, accuracy, and research value.
3. Examples of PICOT Questions
- Why Examples Matter
- Using PICOT question examples helps nursing students, clinicians, and researchers understand how to frame effective evidence-based practice inquiries.
- These examples show how to link the clinical domain, population, intervention, and outcomes into a structured research question.
- Each example clarifies the nature and cause of a health concern, identifies risk factors, and considers the result of the intervention for patient care.
3.1 Diabetes Management
- Example 1: In patients newly diagnosed with diabetes, how does patient education on blood sugar monitoring affect long-term management compared to usual care?
- Explanation:
- Population: Newly diagnosed with diabetes.
- Intervention: Patient education.
- Comparison: Usual care as a control or alternative.
- Outcome: Better management, fewer complications.
- Importance: This shows how PICOT question examples guide prevention and treatment decisions in chronic disease.
3.2 Obesity and Health Risks
- Example 2: Among middle-aged obese adults, what is the increased risk of developing hypertension when following a specific intervention compared to an active control group?
- Explanation:
- Identifies risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
- Uses an intervention vs. a control or alternative.
- Reflects how PICOT question examples help evaluate long-term health outcomes.
3.3 Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness
- Example 3: In pregnant women, does the influenza vaccine during flu season reduce pneumonia risk compared to placebo?
- Explanation:
- Addresses maternal health.
- Demonstrates the role of evidence-based practice in preventive care.
- Shows the result of the intervention when compared to placebo.
- Highlights how PICOT question examples improve safety in vulnerable populations, including Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) considerations for newborns.
3.4 Pain Management
- Example 4: For patients with chronic mechanical neck pain, how does the lateral break diversified technique compare to usual care in terms of pain relief?
- Explanation:
- Focuses on pain compared to standard care.
- Involves select treatments to improve the quality of life.
- Evaluates duration of recovery and outcomes.
- This example illustrates one of the strongest PICOT question examples for musculoskeletal disorders.
3.5 Acute Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis
- Example 5: Among clinicians, how does the use of an advanced diagnostic tool improve accuracy in diagnosing acute myocardial infarction compared to traditional methods?
- Explanation:
- Focuses on being more accurate in diagnosing life-threatening events.
- Focuses on ascertaining injury through evaluation to detect cardiac damage.
- Uses mapping of diagnostic approaches.
- Demonstrates the best available tools in the clinical domain for emergency care.
Practicing with multiple PICOT question examples enhances the ability to formulate structured clinical questions. These examples apply across areas such as diabetes, obesity, infectious disease, pain, and heart health. By aligning with evidence-based practice, they ensure high-quality, and research-driven improvements in patient care.
Elevate Your PICOT Question EBP Essay
Need help structuring your PICOT Question into an EBP essay? Ivy Nursing Help offers top-tier academic support, ensuring clarity, evidence, and precision. Let our professionals guide you—order now for a flawless evidence-based paper!
4. Research Methodology
- Why Research Methodology Matters
- To apply PICOT question examples effectively, it is essential to understand study designs, data collection, and how results impact evidence-based practice.
- A strong methodology ensures that findings are reliable, valid, and applicable to the clinical domain of patient care.
A. Overview of Study Designs (RCT, Observational Studies)
- Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
- Gold standard for testing interventions using PICOT question examples.
- Patients are randomly assigned to an intervention or an active control group.
- Example: In patients newly diagnosed with diabetes, RCTs test whether lifestyle education lowers hypertension rates compared to usual care.
- Ensures results reflect the actualresult of the intervention rather than external influences.
- Observational Studies
- Useful when RCTs are not feasible due to ethics, cost, or practicality.
- Tracks real-world data to understand the nature and cause of outcomes.
- Example: Studying theincreased risk of heart disease in obese adults through long-term observation.
- These designs are valuable for studying risk factors, injury through evaluation, or duration of recovery.
- Specialized Applications
- In the NICU, observational studies help evaluate how premature infants respond to select treatments.
- Diagnostic research uses mapping tools to be more accurate in diagnosing acute conditions like myocardial infarction.
- Both designs illustrate how PICOT question examples facilitate meaningful research across various health areas.
B. Importance of Literature Search to Gather Best Evidence
- Why Literature Search is Essential
- Helps identify the best available studies to answer a PICOT question.
- Ensures that clinical decisions are based on reliable data, not assumptions.
- Example: Reviewing studies on vaccine use during flu season to assess effectiveness in pregnancy.
- Steps in Literature Search
- Define a focused research question using the PICOT format.
- Search reputable databases for studies aligned with PICOT question examples.
- Compare interventions with control or alternative treatments.
- Assess outcomes like pain compared to standard care or reductions in hypertension rates.
- Contribution to Evidence Based Practice
- Strengthens patient care decisions with high-quality information.
- Links study results directly to the clinical domain of nursing and medicine.
- Shows how structured methodology, supported by PICOT question examples, ensures safer, more effective care strategies.
Methodology is the backbone of applying the PICOT question examples. By combining RCTs, observational studies, and comprehensive literature searches, healthcare providers ensure research is reliable, clinically relevant, and truly evidence-based practice.
6. Types of PICOT Questions and Examples
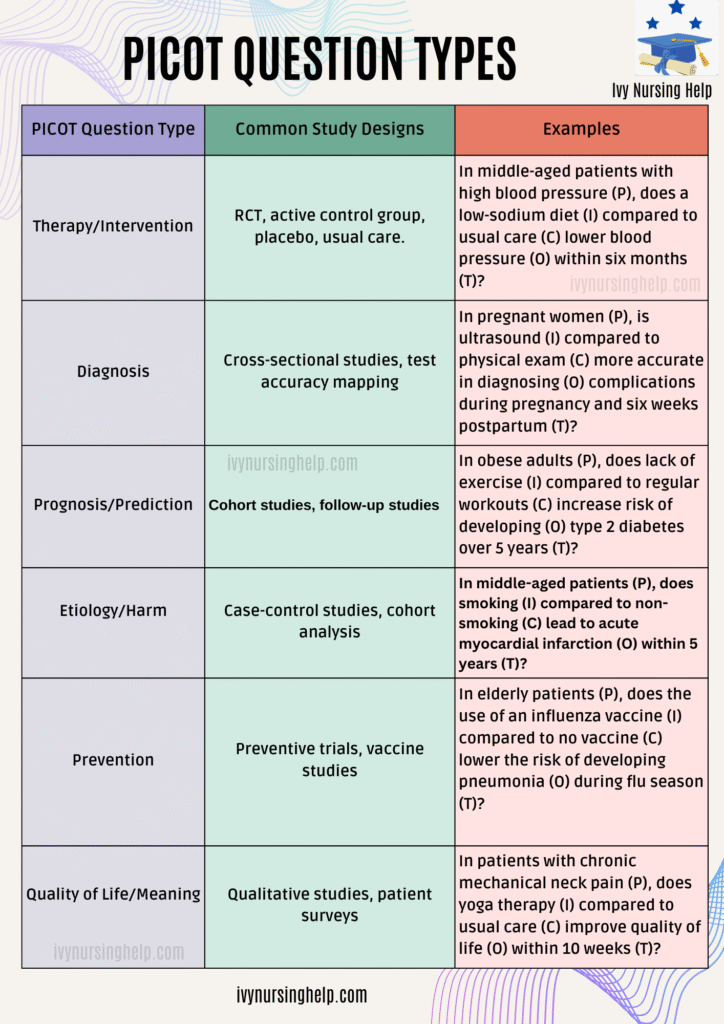
A. Describe the Different Types of PICOT Questions
- Therapy/Intervention – Focus on whether a treatment or intervention achieves the best result. Example: lowering blood sugar levels in patients newly diagnosed with diabetes.
- Diagnosis – Assess how accurate a particular test or tool is in diagnosing a condition. Example: comparing physical examination with X-rays in pneumonia.
- Prognosis/Prediction – Explore the nature and cause of a disease outcome and the duration of recovery. Example: Patient education for those who are obese with high blood pressure.
- Etiology/Harm – Identify risk factors and the increased risk of developing conditions. Example: pregnant women and the risk of developing complications during pregnancy and six weeks postpartum.
- Prevention – Select treatments that prevent disease. Example: use of an influenza vaccine to reduce the risk of developing pneumonia in the flu season.
- Quality of Life/Meaning – Understand how pain compared to usual care impacts quality of life. Example: chronic mechanical neck pain and pain relief therapies.
B. Common Study Designs for Each Type of PICOT Question
- Therapy/Intervention → RCT (randomized controlled trial), active control group vs placebo.
- Diagnosis → Cross-sectional study, mapping clinical domain accuracy through literature search.
- Prognosis → Cohort study, tracking middle-aged patients with obesity over the years.
- Etiology/Harm → Case-control study, examining injury through evaluation of risk factors.
- Prevention → RCT or longitudinal study, evaluating influenza vaccine during flu season.
- Quality of Life → Qualitative study design, exploring patient care in NICU or pain relief strategies.
C. Key Features and When They Are Used
- Evidence-based practice – Always grounded in best evidence from a literature search.
- Control or alternative – Intervention must be compared with placebo or usual care.
- Research methodology – Must align with clinical question and clinical domain.
- Patient care focus – Clinicians and researchers use the PICOT framework to improve patient care.
- Mapping to study design – Therapy → RCT; Diagnosis → accuracy studies; Prognosis → cohort; Prevention → controlled trials; Harm → case-control.
- Best available evidence – Ensures clinicians select treatments that are safe and effective.
- Therapy Questions – Best used when testing selected treatments; looking for the result of the intervention through an RCT.
- Diagnosis Questions – Applied when clinicians need the best available tool that is accurate in diagnosing.
- Prognosis Questions – Useful when assessing the increased risk of disease progression, e.g., in obese or middle-aged patients.
- Etiology Questions – Applied to identify risk of developing conditions such as pneumonia or hypertension.
- Prevention Questions – Used when evaluating vaccines,patient education, or strategies to minimize harm.
- Quality of Life Questions – Applied in NICU settings, chronic disease management, or therapies like the lateral break diversified technique for musculoskeletal conditions.
D. Detailed PICOT Question Examples
Here are several PICOT Question examples compiled by a team of seasoned nursing writers at ivynursinghelp.com. We write evidence-based research essays and papers at affordable rates:
Therapy/Intervention
- In middle-aged patients with high blood pressure (P), does a low-sodium diet (I) compared to usual care (C) lower blood pressure (O) within six months (T)?
- In patients with chronic mechanical neck pain (P), does the lateral break diversified technique (I) compared to placebo (C) improve pain relief (O) within 8 weeks (T)?
- In patients recovering from acute myocardial infarction (P), does cardiac rehab (I) compared to no rehab (C) reduce the duration of recovery (O) over 12 months (T)?
Diagnosis
- In pregnant women (P), is ultrasound (I) compared to physical examination (C) more accurate in diagnosing (O) complications during pregnancy and six weeks postpartum (T)?
- In patients newly diagnosed with diabetes (P), is HbA1c (I) compared to fasting blood sugar levels (C) more effective in diagnosing poor control (O) within the first year (T)?
- In patients suspected of pneumonia (P), is chest X-ray (I) compared to auscultation (C) more reliable in making a correct diagnose (O) during initial admission (T)?
Prognosis/Prediction
- In obese adults (P), does a lack of exercise (I) compared to regular workouts (C) increase the risk of developing (O) type 2 diabetes over 5 years (T)?
- In NICU infants (P), does premature birth (I) compared to full-term (C) lead to an increased risk (O) of complications during the first year (T)?
- In clinicians and researchers’ patient follow-up studies, do hypertension patients (P) with the exposure of hypertension (I) compared to normotensive patients (C) show worse outcomes (O) over a period of 10 years (T)?
Etiology/Harm
- In obese individuals (P), does sedentary lifestyle (I) compared to active lifestyle (C) increase the risk of developing (O) cardiovascular disease within 10 years (T)?
- In pregnant women (P), does alcohol use (I) compared to abstinence (C) lead to fetal harm (O) by six weeks postpartum (T)?
- In middle-aged patients (P), does smoking (I) compared to non-smoking (C) lead to a higher incidence of acute myocardial infarction (O) within 5 years (T)?
Prevention
- In elderly patients (P), does the use of an influenza vaccine (I) compared to no vaccine (C) lower the risk of developing pneumonia (O) during flu season (T)?
- In adults with obesity (P), does patient lifestyle counseling (I) compared to no counseling (C) reduce risk factors (O) for diabetes over 3 years (T)?
- In patient education programs (P), does counseling (I) compared to self-learning (C) improve prevention of hypertension (O) within 12 months (T)?
Quality of Life/Meaning
- In patients with chronic mechanical neck pain (P), does yoga therapy (I) compared to usual care (C) improve quality of life (O) within 10 weeks (T)?
- In post-surgical patients (P), does music therapy (I) compared to no therapy (C) provide greater pain relief (O) during recovery (T)?
- In cancer patients (P), does mindfulness training (I) compared to active control group (C) improve emotional well-being (O) over 8 weeks (T)?
7. Conclusion
- Summary of Relevance in Clinical Practice
- PICOT question examples are essential for framing strong clinical and nursing research.
- They provide a structured way to create a focused research question that improves patient care.
- By using the PICOT framework, clinicians can evaluate interventions and outcomes across many areas:
- Pregnancy and six weeks postpartum: Example questions can address whether the use of an influenza vaccine lowers the risk of developing pneumonia compared to a placebo.
- Diabetes management: PICOT helps assess how education on blood sugar levels affects patients newly diagnosed with diabetes.
- Cardiovascular health: Questions framed with PICOT identify how lifestyle changes reduce high blood pressure and long-term complications.
- These examples highlight how PICOT question examples connect research with clinical needs, making practice more evidence-based.
- Encouragement for Clinicians and Researchers
- PICOT question examples should be applied regularly to strengthen evidence-based practice.
- They make it easier to compare treatments, analyze the results of the intervention, and measure effectiveness in real patient scenarios.
- Practical benefits include:
- Better identification of risk factors for chronic and acute diseases.
- Improved decision-making through clarity and structured inquiry.
- Support for creating policies and guidelines that reflect the best available evidence.
- Clinicians and researchers are encouraged to:
- Formulate clear and focused questions using PICOT.
- Use picot question examples as a template to design stronger studies.
- Integrate findings into clinical settings, from NICU studies to community health.
PICOT question examples bridge the gap between theory and practice. They help frame studies in areas such as blood sugar levels, high blood pressure, and maternal health during pregnancy and six weeks postpartum. By applying structured PICOT methods, clinicians and researchers improve outcomes, reduce the risk of developing conditions such as pneumonia, and build safer, more effective care.
FAQs: PICOT Question Examples
1. What is the purpose of PICOT in nursing research?
- The purpose of PICOT is to frame a clear and focused research question.
- PICOT question examples ensure inquiries are precise, measurable, and clinically relevant.
- They guide evidence-based practice by aligning patient problems with interventions and outcomes.
- Example: In patients newly diagnosed with diabetes, does lifestyle coaching lower blood sugar compared to medication alone?
2. How do PICOT questions support evidence-based practice?
- PICOT question examples connect clinical issues with the best available research.
- They help identify risk factors, compare select treatments, and evaluate results.
- By testing interventions against a control or alternative, nurses improve patient care.
- Example: During flu season, does vaccination reduce complications in pregnant women compared to a placebo?
3. Can PICOT questions address pain and recovery outcomes?
- Absolutely. PICOT question examples can focus on pain compared to usual care or therapy.
- They can evaluate the duration of recovery after surgery or injury.
- They explore the results of an intervention, such as faster healing or improved function.
- Example: In orthopedic patients, does physical therapy vs. standard care shorten recovery time?
4. How do PICOT questions apply in diagnostic accuracy?
- They can measure how new tools are more accurate in diagnosing complex conditions.
- Useful in cardiac care, stroke evaluation, and even NICU studies.
- They examine the nature and cause of conditions and ensure better injury prevention through evaluation.
- Example: Among clinicians, does advanced imaging improve the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction compared to standard methods?
5. What clinical domains benefit most from PICOT question examples?
- Chronic disease management (diabetes, hypertension, obesity).
- Infectious disease prevention (vaccine effectiveness in flu season).
- Emergency care (injury through evaluation, acute events).
- Pediatric and neonatal care (NICU studies, mapping interventions).
- Each domain benefits because the PICOT question examples ensure reliable, research-backed outcomes.
